Imaging stroboscopico ultraveloce con strisce RF in un microscopio elettronico a trasmissione commerciale
-
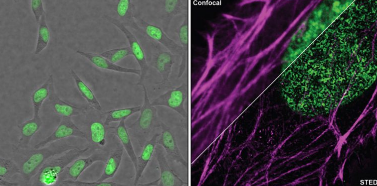
- Lo sviluppo della microscopia elettronica ultraveloce (UEM), in particolare l’imaging stroboscopico, ha portato lo studio della dinamica strutturale a un nuovo livello, superando i limiti spaziali della spettroscopia ultraveloce e i limiti di tempo della tradizionale TEM. La combinazione dei concetti che governano entrambe le tecniche ha consentito la visualizzazione diretta della dinamica con risoluzioni spazio-temporali nel regime del picosecondo-nanometro. Qui spostiamo i limiti dell’imaging del fascio di elettroni pulsati tramite la deflessione trasversale indotta da RF basata su un generatore di impulsi a striscia di frequenza regolabile da 200 keV di nuova concezione.
- Presentiamo una risoluzione spaziale di 0,2 nm e spieghiamo le mappe di induzione dello spin magnetico mediante microscopia di fase. Presentiamo anche misurazioni della coerenza del fascio ed estendiamo il nostro studio utilizzando le modalità di respirazione del pettine di silicio di eccitazione RF, che forniscono una migliore tempistica tra il treno di impulsi di elettroni e il campo elettrico. È stato inoltre sviluppato un nuovo dispositivo RF con impedenza corrispondente al segnale RF per ridurre al minimo la perdita di potenza di trasmissione ai campioni e le sue prestazioni sono paragonate a quelle di un dispositivo campione convenzionale.

Test del lettore di schede fototermico utilizzando una striscia reattiva in oro colloidale disponibile in commercio per il rilevamento quantitativo rapido dei rischi alimentari
- La semplice e veloce striscia reattiva in oro colloidale disponibile in commercio può essere utilizzata solo per il rilevamento qualitativo o semiquantitativo con scarsa rilevabilità e risultati falsi negativi. Questo documento sviluppa una striscia reattiva fototermica che combina la striscia reattiva con un lettore di schede fototermico portatile per ottenere un rilevamento quantitativo con un’eccellente rilevabilità. Secondo l’effetto fototermico prodotto dalle nanoparticelle d’oro (GNP) catturate sulla linea di test, il segnale potrebbe essere catturato da un lettore.
- Sono stati studiati tredici rischi alimentari, inclusi residui di farmaci veterinari e residui di pesticidi; la rilevabilità fototermica nei campioni effettivi era di circa 23 (paration metilico), 7 (enrofloxacina), 6 (sarafloxacina), 8 (sulfadiazina), 12 (sulfametazina), 7 (paraquat), 6 (verde malachite), 11 (amantadina), 13 (nitrofurazone), 6 (dietilstilbestrolo), 12 (estriolo), 21 (estrone) e 26 (17β-estradiolo) volte meglio del rilevamento visivo. I nostri risultati hanno mostrato che la striscia reattiva fototermica può essere utilizzata per il rilevamento sensibile, rapido e quantitativo dei residui di rischio alimentare.
Acetato di cellulosa e nanocomposito di cellulosa immobilizzati con il cromoforo DCDHF-idrazone verso una striscia reattiva intelligente per il rilevamento colorimetrico del dietilclorofosfato come fattore nervoso mimico
- L’esposizione agli agenti nervini, che di solito sono gas incolori e inodori, può causare insufficienza d’organo, paralisi e persino morte rapida. Il dietilclorofosfato (DCP) è stato riconosciuto come uno dei più noti imitatori di fattori nervosi nel combattimento chimico. Nel presente studio, presentiamo una semplice strategia per sviluppare una striscia microporosa portatile e reversibile basata su nanocompositi per il rilevamento a occhio nudo di DCP in pochi secondi. Il cromoforo di dicianometilene diidrofuranidrazone (DCDHF-H) è stato sintetizzato mediante una facile reazione di accoppiamento azoico e incapsulato in situ durante la preparazione di nanocompositi di acetato di cellulosa / nanowiskers di cellulosa / idrazone (CA-CNW-H).
- Questi nanocompositi CA-CNW-H hanno mostrato uno spostamento batocromico dell’intensità di assorbimento di circa 142 nm da 438 a 580 nm con l’aumento della concentrazione di DCP. L’attuale striscia sensore CA-CNW-H ha mostrato un limite di rilevamento per DCP compreso tra 25 e 200 ppm. Il cambiamento di colore di CA-CNW-H da giallo a viola dopo l’esposizione a DCP è stato rilevato dall’analisi di CIE Lab. Sono state esaminate la morfologia, la cristallinità fibrosa, la stabilità termica e le proprietà meccaniche delle strisce di sensori CA-CNW-H preparate.
Sviluppo di una test card basata su strisce immunocromatografiche d’oro colloidale per la rilevazione rapida di anticorpi contro Theileria equi e Babesia caballi.
- La piroplasmosi equina (EP) è un problema serio nell’industria equina e il controllo dell’EP è fondamentale per il commercio internazionale di cavalli. L’EP è causato da due protozoi apicomplessi, Theileria equi e Babesia caballi. Metodi rapidi e accurati adatti per rilevare questi parassiti sul campo sono fondamentali per controllare l’infezione e la diffusione di EP. In questo studio abbiamo sviluppato una scheda per la rilevazione degli anticorpi contro T. equi e B. caballi basata su due strisce immunocromatografiche in oro colloidale secondo il principio del double sandwich antigen. Le proteine dell’antigene 1 (EMA1) dell’equimerozoite e la proteina rhoptry BC48 sono comunemente usate come antigeni diagnostici rispettivamente contro T. equi e B. caballi. La proteina EMA1 o BC48 purificata marcata con oro colloidale è stata utilizzata come rivelatore sulla striscia,
- Il protocollo richiede da 10 a 15 minuti e non richiede apparecchiature o prodotti chimici specializzati e un test può rilevare due agenti patogeni EP su una scheda. I test di specificità hanno confermato la mancanza di reattività crociata con sieri positivi per i comuni patogeni equini. Utilizzando un kit commerciale per l’immunosorbente enzimatico (cELISA) per il confronto, 476 campioni clinici sono stati testati mediante card. I tassi di coincidenza erano rispettivamente del 96,43% e del 97,90% per T. equi e B. caballi. Il feedback delle prove sul campo è stato costantemente positivo, suggerendo che questo strumento diagnostico può essere utile per controllare la diffusione di T. equi e B. caballi.
- La piroplasmosi equina (EP), causata da Theileria equi e Babesia caballi, è una grave malattia trasmessa dalle zecche nei cavalli che si verifica nella maggior parte del mondo. Il PE è considerato una malattia soggetta a denuncia dall’Organizzazione mondiale per la salute animale (OIE). La diagnosi accurata e la differenziazione di T. equi e B. caballi sono molto importanti per la prevenzione, il controllo e il trattamento dell’EP. Ecco perché abbiamo sviluppato il test immunocromatografico Colloidal Gold Sandwich (GICG) per la rilevazione di T. equi e B. caballi. Due strisce GICG sono state impilate una accanto all’altra su una scheda di rilevamento di T. equi e B. caballi e in un test è stato possibile rilevare due agenti patogeni EP. Il metodo era semplice, veloce e specifico per la rilevazione di EP; pertanto, rispetto ai metodi precedenti, questo metodo è più adatto per la diagnostica dei patogeni sul campo.
Strisce immunocromatografiche fluorescenti ad alta specificità nel tempo per la rilevazione simultanea di diversi pesticidi organofosforici in base alla strategia della sonda indiretta
- L’uso indiscriminato di pesticidi organofosforici (PO) rappresenta un’enorme minaccia per la sicurezza alimentare, la salute umana e l’ambiente. Poiché esistono molti tipi di pesticidi, individuarli è una sfida. Il rilevamento simultaneo di più organofosfati in un test è attualmente un problema da risolvere. In questo articolo, è stata preparata una striscia di immunocromatografia a fluorescenza a risoluzione temporale (TRFIA) utilizzando anticorpi OP ad ampia specificità (Abs) come elemento di riconoscimento. Gli addominali sono stati combinati con microsfere di lattice di ossido di europio con anticorpi anti-topo di pecora (SaMIgG) per creare una sonda indiretta.
- Questa strategia può realizzare efficacemente l’amplificazione del segnale e può risparmiare la quantità e proteggere l’attività degli addominali. Al rilevamento, è stato osservato un cambiamento di colore della linea del test (linea T) per la valutazione qualitativa alla luce UV (365 nm). Le immagini campione positive sono state quindi analizzate utilizzando ImageJ per completare il rilevamento quantitativo. In condizioni di progettazione e funzionamento ottimali, il limite di rilevamento della striscia può raggiungere 0,53 ng g -1 .
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG06F-PA/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.36 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG09F-PG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.22 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG09F-PG/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.36 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG11F-WG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.01 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG11F-WG/W
Biomat
1 plate
28.05 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG21F-NA
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.22 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG21F-NA/W
Biomat
1 plate
26.84 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG0STF-SA5/200
Biomat
1 plate
23.32 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG0STF-SA5/200/W
Biomat
1 plate
26.84 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG08F-PAG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
37.4 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG08F-PAG/W
Biomat
1 plate
51.37 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG07F-CON_A
Biomat
1 plate
15.18 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG07F-CON_A/W
Biomat
1 plate
20.46 EUR
Poly-L-lysine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG12F-LYS-L
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
15.4 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG20F-HC3
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.7 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG20F-HC3/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Poly-L-arginine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG13F-AR
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.01 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG18F-HC1
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
17.49 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG18F-HC1/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.56 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG19F-HC2
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.7 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG19F-HC2/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG25F-aM
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
32.67 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG25F-aM/W
Biomat
1 plate
38.5 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG26F-aR
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
28.05 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MG26F-aR/W
Biomat
1 plate
33.88 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MGSTDF-SB75/100
Biomat
1 plate
25.74 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Clear PS
MGSTDF-SB75/100/W
Biomat
1 plate
29.15 EUR
High Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (Clear)
BSV-MG01F-HB8
BioServUK
100 pcs
606 EUR
Medium Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (Clear)
BSV-MG0F-MB
BioServUK
100 pcs
566 EUR
No Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB03F2-NB
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
10.78 EUR
No Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW03F-NB
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
10.78 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGB0STF2-SA5-200
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
265.07 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGB0STF2-SA5-200-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
299.09 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGB15F2-BIO-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
287.75 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGW0STF-SA5-200
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
265.07 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGW0STF-SA5-200-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
299.09 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MGW15F-BIO-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
287.75 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MG0STF-SA5-200
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
262.8 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MG0STF-SA5-200-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
296.82 EUR
96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame
MG15F-BIO-W
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
285.48 EUR
High Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB01F2-HB8
Biomat
1 plate
3.74 EUR
High Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW01F-HB8
Biomat
1 plate
3.74 EUR
Carboxylated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB04F2-COOH
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
14.3 EUR
Carboxylated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW04F-COOH
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
14.3 EUR
Amine Treated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB02F2-AM1
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Medium Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB0F2-MB
Biomat
1 plate
3.52 EUR
Jacalin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB10F2-JAC
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
17.82 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB15F2-BIO
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB15F2-BIO/W
Biomat
1 plate
25.96 EUR
Amine Treated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW02F-AM1
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Medium Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW0F-MB
Biomat
1 plate
3.52 EUR
Jacalin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW10F-JAC
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
17.82 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW15F-BIO
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW15F-BIO/W
Biomat
1 plate
25.96 EUR
Maleimide Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB22F2-MAL
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
28.27 EUR
Maleimide Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW22F-MAL
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
28.27 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB06F2-PA
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB06F2-PA/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.58 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB09F2-PG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB09F2-PG/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.58 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB11F2-WG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB11F2-WG/W
Biomat
1 plate
28.27 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW06F-PA
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW06F-PA/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.58 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW09F-PG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW09F-PG/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.58 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW11F-WG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW11F-WG/W
Biomat
1 plate
28.27 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB21F2-NA
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB21F2-NA/W
Biomat
1 plate
27.06 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW21F-NA
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
22.44 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW21F-NA/W
Biomat
1 plate
27.06 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB0STF2-SA5/200
Biomat
1 plate
23.65 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB0STF2-SA5/200/W
Biomat
1 plate
27.06 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW0STF-SA5/200
Biomat
1 plate
23.65 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW0STF-SA5/200/W
Biomat
1 plate
27.06 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB08F2-PAG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
37.95 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB08F2-PAG/W
Biomat
1 plate
51.59 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW08F-PAG
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
37.95 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW08F-PAG/W
Biomat
1 plate
51.59 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB07F2-CON_A
Biomat
1 plate
15.4 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB07F2-CON_A/W
Biomat
1 plate
20.79 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW07F-CON_A
Biomat
1 plate
15.4 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW07F-CON_A/W
Biomat
1 plate
20.79 EUR
Poly-L-lysine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB12F2-LYS-L
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
15.73 EUR
Poly-L-lysine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW12F-LYS-L
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
15.73 EUR
Poly-L-arginine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB13F2-AR
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB18F2-HC1
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
17.82 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB18F2-HC1/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB19F2-HC2
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB19F2-HC2/W
Biomat
1 plate
22 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB20F2-HC3
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB20F2-HC3/W
Biomat
1 plate
22 EUR
Poly-L-arginine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW13F-AR
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
21.23 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW18F-HC1
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
17.82 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW18F-HC1/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW19F-HC2
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW19F-HC2/W
Biomat
1 plate
22 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW20F-HC3
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
18.92 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW20F-HC3/W
Biomat
1 plate
22 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB25F2-aM
Biomat
1 plate
32.89 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB25F2-aM/W
Biomat
1 plate
38.72 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB26F2-aR
Biomat
1 plate
28.27 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGB26F2-aR/W
Biomat
1 plate
34.1 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW25F-aM
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
32.89 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW25F-aM/W
Biomat
1 plate
38.72 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW26F-aR
Biomat
10 plates(2X5 plates in a transparent bag)
28.27 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGW26F-aR/W
Biomat
1 plate
34.1 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGBSTDF2-SB75/100
Biomat
1 plate
25.96 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - Black PS
MGBSTDF2-SB75/100/W
Biomat
1 plate
29.48 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGWSTDF-SB75/100
Biomat
1 plate
25.96 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame - White PS
MGWSTDF-SB75/100/W
Biomat
1 plate
29.48 EUR
High Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (Black)
BSV-MGB01F2-HB8
BioServUK
100 pcs
647 EUR
High Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (White)
BSV-MGW01F-HB8
BioServUK
100 pcs
647 EUR
Medium Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (Black)
BSV-MGB0F2-MB
BioServUK
100 pcs
606 EUR
Medium Binding Capacity - 96 well plates - 12x8 Well Breakable Strips on single well holding frame (White)
BSV-MGW0F-MB
BioServUK
100 pcs
606 EUR
Testosterone ELISA, Breakable Well
GWB-472DB9
GenWay Biotech
96 Tests
Ask for price
8-well PCR Strip Tubes, Clear
27-425
Genesee Scientific
Box of 125 Strips/Unit
67.53 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse, 1 x 8 Strip Well, Clear Coated 96 Well Plate, 1EA
X012-1EA
Arbor Assays
1EA
48 EUR
Break-2-ways Plate Breakable - PK50
PCR1280
Scientific Laboratory Supplies
PK50
454.95 EUR
No Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT03F4-NB
Biomat
1 plate
10.56 EUR
Carboxylated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT04F4-COOH
Biomat
1 plate
14.08 EUR
High Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT01F4-HB8
Biomat
1 plate
3.52 EUR
Amine Treated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT02F4-AM1
Biomat
1 plate
21.01 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT15F4-BIO
Biomat
1 plate
18.7 EUR
Biotin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT15F4-BIO/W
Biomat
1 plate
25.74 EUR
Medium Binding 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT0F4-MB
Biomat
1 plate
3.3 EUR
Jacalin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT10F4-JAC
Biomat
1 plate
17.49 EUR
Maleimide Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT22F4-MAL
Biomat
1 plate
28.05 EUR
0.2ml 8-Strip Tubes & Flat Strip Caps, Clear
24-706
Genesee Scientific
Box of 125 Tubes & Caps/Unit
74.53 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT0STF4-SA5/200
Biomat
1 plate
23.32 EUR
Streptavidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT0STF4-SA5/200/W
Biomat
1 plate
26.84 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT21F4-NA
Biomat
1 plate
22.22 EUR
Neutravidin Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT21F4-NA/W
Biomat
1 plate
26.84 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT06F4-PA
Biomat
1 plate
22.22 EUR
Protein A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT06F4-PA/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.36 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT09F4-PG
Biomat
1 plate
22.22 EUR
Protein G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT09F4-PG/W
Biomat
1 plate
30.36 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT11F4-WG
Biomat
1 plate
21.01 EUR
Wheat Germ Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT11F4-WG/W
Biomat
1 plate
28.05 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT08F4-PAG
Biomat
1 plate
37.4 EUR
Protein A/G Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT08F4-PAG/W
Biomat
1 plate
51.37 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT07F4-CON_A
Biomat
1 plate
15.18 EUR
Concanavalin A Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT07F4-CON_A/W
Biomat
1 plate
20.46 EUR
0.2mL Clear Polypropylene PCR Tubes 8 Well Strips - PK300
6542
Scientific Laboratory Supplies
PK300
726.3 EUR
0.2ml 8-Strip Tubes and Dome Strip Caps, Clear
24-705
Genesee Scientific
Box of 125 Tubes and Caps/Unit
69.27 EUR
Poly-L-lysine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT12F4-LYS-L
Biomat
1 plate
15.4 EUR
Poly-L-arginine Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT13F4-AR
Biomat
1 plate
21.01 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT18F4-HC1
Biomat
1 plate
17.49 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC1 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT18F4-HC1/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.56 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT19F4-HC2
Biomat
1 plate
18.7 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC2 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT19F4-HC2/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT20F4-HC3
Biomat
1 plate
18.7 EUR
Heparin Catcher HC3 Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT20F4-HC3/W
Biomat
1 plate
21.78 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT25F4-aM
Biomat
1 plate
32.67 EUR
Goat anti-Mouse IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT25F4-aM/W
Biomat
1 plate
38.5 EUR
Nickel Coated Plates, Clear, 12×8-Well Strips, White Frame
SP-16
ACROBIOSYSTEMS
1plate
310.3 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT26F4-aR/W
Biomat
1 plate
33.88 EUR
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MT26F4-aR_
Biomat
1 plate
28.05 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MTSTDF4-SB75/100
Biomat
1 plate
25.74 EUR
Streptavidin High Binding Coated - 96 well plates - 8 Well Strips on 12 x 8 frame - Clear PS
MTSTDF4-SB75/100/W
Biomat
1 plate
29.15 EUR
Streptavidin Coated Plates, Clear, 12×8-Well Strips, White Frame
SP-11
ACROBIOSYSTEMS
1plate
149.8 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL CLEAR PCR STRIP TUBES AND CLEAR STRIP CAPS.
PCR-0208-CP-C
CORNING
125/pk
777.6 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL CLEAR PCR STRIP TUBES AND CLEAR STRIP CAPS.
PCR-0208-CP-C-100
CORNING
100/pk
133.2 EUR
8-Strip PCR Tube with cap - Clear
PR12-1X200NO
EWC Diagnostics
1 unit
88.06 EUR
0,1ML THIN WALL TUBES 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR
PCR-0108-LP-C
CORNING
125/pk
724.8 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL TUBES 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR
PCR-0208-C
CORNING
125/pk
724.8 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL TUBES 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR
PCR-0208-C-100
CORNING
100/pk
106.8 EUR
8 Strip PCR Tubes Clear-600 Str - PK600
PCR1000
Scientific Laboratory Supplies
PK600
203.85 EUR
8-Strip PCR Tube without cap - Clear
PR14-1X200NO
EWC Diagnostics
1 unit
73.42 EUR
8-Strip Ultra Clear Caps, 120 Strips of 8 Caps
GP407
GenDepot
960 caps
148.8 EUR
0,1ML THIN WALL TUBES 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR & REAL TIME STRIP CAPS
PCR-0108-LP-RT-C
CORNING
125/pk
850.8 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL TUBE CAPS 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR
PCR-02CP-C
CORNING
125/pk
174 EUR
0.2ML THIN WALL TUBE CAPS 8 PER STRIP. CLEAR
PCR-02CP-C-100
CORNING
100/pk
56.4 EUR
E la striscia TRFIA si è comportata bene nel test additivo di campioni vegetali. È poco costoso da preparare, comodo da trasportare e facile da maneggiare. Ancora più importante, migliora l’efficienza di rilevamento e soddisfa le esigenze di test rapidi sul campo di un gran numero di campioni.